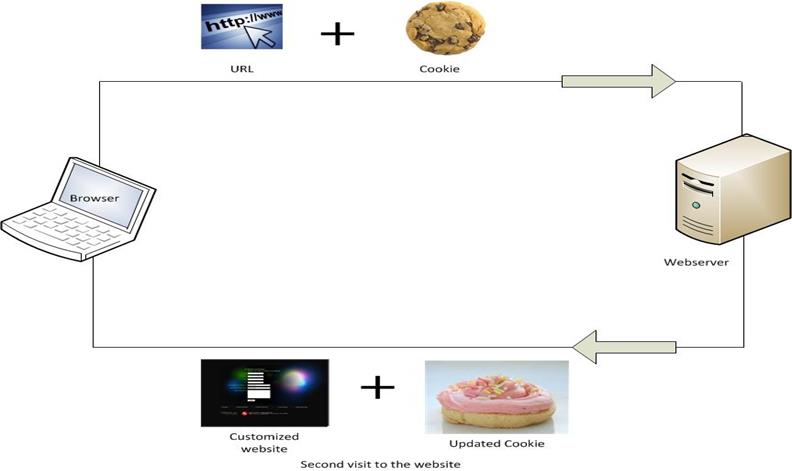
What Cookies Are
At this point, just about everyone has heard of internet cookies, but what do they actually do? According to Tom Scott,[1] cookies are client-side storage: information stored on a user’s computer instead of a website’s servers. When a browser sends a request to a website, it also sends any cookies that it has received from that website, and the website can use the information in those cookies to change the webpage that it sends back. The website can also send the browser new cookies, which the browser saves for the next time it requests a page from the website. Webopedia[2] explains that there are two types of cookies. The first type are called “session cookies,” and they are deleted when the browser is closed. Session cookies are used for session identification but usually not user information. The other type of cookies, called “persistent cookies,” can stay on a user’s device for much longer. Persistent cookies are stored on a computer’s hard drive until their respective expiration dates, and they are normally used to store user preferences on a website or information that can identify users.
Cookie Security Problems
The website that a user is directly visiting is not the only one that can store cookies on a user’s device; content from other websites that appears on the site a user is viewing, such as embedded social media posts and ads, can generate its own cookies. Kaspersky[3] states that first-party cookies, which are made by the main website, are usually safe, especially on reputable and safe websites. Third-party cookies, however, can be used to track individuals across the internet. For example, if an advertising company has ads on several different websites, it can tell when individual users go to each of those sites. According to Infosec,[4] there are also several different ways that websites can access a user’s cookies from other websites. These may include embedding links to other sites, placing scripts in cookies, making cookies for subdomains, and setting too many cookies for the browser to store.
How to Keep Your Cookies Safe
The number of different ways attackers try to steal information from cookies can be intimidating; fortunately, there are several actions users can take to prevent such attacks. Security Boulevard[5] outlines a few ways that website visitors can protect themselves from cookie-stealing. Using an antivirus software can alert users to and remove potentially harmful cookies installed by websites. Visitors to websites should also avoid following suspicious links and storing sensitive data on websites; data entered by a user would probably be stored on a cookie that would be vulnerable to stealing. In addition to this, users can clear their cookies to remove sensitive information stored on them, which can be done through the settings of most browsers. OnlineCmag[6] adds that some browsers have settings that can control which sites can use cookies, or that can block third-party cookies. Furthermore, some browser extensions can give users even greater control over their cookies. Using these methods, visitors to websites can ensure that they stay safe from attacks that could steal their information from their cookies.
